一、AIDL是什么
AIDL全称是Android Interface Definition Language,也就是Android接口定义语言。
二、AIDL是干什么的
设计这门语言的目的是为了实现进程间通信,尤其是在涉及多进程并发情况下的进程间通信。
Android中其他进程间通信的方式
Bundle、文件共享、、ContentProvider、Socket、BroadcastReceiver,每种方式都有自己的特点,这里不做过多的扩展。
三、AIDL怎么用
1、AIDL语法
文件类型
用AIDL书写的文件的后缀是 .aidl。
数据类型
- 基本数据类型(byte,short,int,long,float,double,boolean,char)
- String 和 CharSequence
- List:只支持ArrayList,里面每个元素都必须能被AIDL支持
- Map:只支持HashMap,里面的Key和Value都必须能被AIDL支持
- Parcelable:所有实现Parcelable接口的对象
- AIDL:所有的AIDL接口本身也可以在AIDL文件中使用
注意:
在编写AIDL文件时,自定义的Parcelable对象必须显示 import ,不管它是否和当前AIDL文件位于同一个包内。
比如,现在我们编写了两个文件,一个叫做 Book.java ,另一个叫做 BookManager.aidl,它们都在 com.wangyanan.aidldemo 包下。现在我们需要在 .aidl 文件里使用 Book 对象,那么我们就必须在 .aidl 文件里面写上 import com.wangyanan.aidldemo.Book 。
定向tag
AIDL中的定向 tag 表示了在跨进程通信中数据的流向,其中 in 表示数据只能由客户端流向服务端, out 表示数据只能由服务端流向客户端,而 inout 则表示数据可在服务端与客户端之间双向流通。
其中,数据流向是针对在客户端中的那个传入方法的对象而言的。
in 为定向 tag 的话表现为服务端将会接收到一个那个对象的完整数据,但是客户端的那个对象不会因为服务端对传参的修改而发生变动;
out 的话表现为服务端将会接收到那个对象的的空对象,但是在服务端对接收到的空对象有任何修改之后客户端将会同步变动;
inout 为定向 tag 的情况下,服务端将会接收到客户端传来对象的完整信息,并且客户端将会同步服务端对该对象的任何变动。
2、具体操作
AIDL代码
|
|
|
|
|
|
注意:这里有一个坑!大家可能注意到了,在 Book.aidl 文件中,我一直在强调:Book.aidl与Book.java的包名应当是一样的。这似乎理所当然的意味着这两个文件应当是在同一个包里面的——事实上,很多比较老的文章里就是这样说的,他们说最好都在 aidl 包里同一个包下,方便移植——然而在 Android Studio 里并不是这样。如果这样做的话,系统根本就找不到 Book.java 文件,从而在其他的AIDL文件里面使用 Book 对象的时候会报 Symbol not found 的错误。为什么会这样呢?因为 Gradle 。Android Studio 是默认使用 Gradle 来构建 Android 项目的,而 Gradle 在构建项目的时候会通过 sourceSets 来配置不同文件的访问路径,从而加快查找速度。Gradle 默认是将 java 代码的访问路径设置在 java 包下的,这样一来,如果 java 文件是放在 aidl 包下的话那么理所当然系统是找不到这个 java 文件的。那应该怎么办呢?
即要 java 文件和 aidl 文件的包名是一样的,又要能找到这个 java 文件——那么仔细想一下的话,其实解决方法是很显而易见的。首先我们可以把问题转化成:如何在保证两个文件包名一样的情况下,让系统能够找到我们的 java 文件?这样一来思路就很明确了:要么让系统来 aidl 包里面来找 java 文件,要么把 java 文件放到系统能找到的地方去,也即放到 java 包里面去。
方法一
修改 build.gradle 文件:在 android{} 中间加上下面的内容。
也就是把 java 代码的访问路径设置成了 java 包和 aidl 包,这样一来系统就会到 aidl 包里面去查找 java 文件,也就达到了我们的目的。只是有一点,这样设置后 Android Studio 中的项目目录会有一些改变,我感觉改得挺难看的。
|
|
方法二
把 java 文件放到 java 包下去:把 Book.java 放到 java 包里任意一个包下,保持其包名不变,与 Book.aidl 一致。只要它的包名不变,Book.aidl 就能找到 Book.java ,而只要 Book.java 在 java 包下,那么系统也是能找到它的。但是这样做的话也有一个问题,就是在移植相关 .aidl 文件和 .java 文件的时候没那么方便,不能直接把整个 aidl 文件夹拿过去完事儿了,还要单独将 .java 文件放到 java 文件夹里去。
服务端代码
|
|
AIDLService是服务端代码,大致可以分为三块:第一块是初始化,在 onCreate() 方法里面我进行了一些数据的初始化操作。第二块是重写 BookManager.Stub 中的方法(在这里面实现AIDL里面定义的方法接口的具体实现逻辑)。第三块是重写 onBind() 方法,在里面返回写好的 BookManager.Stub 。
接下来在 Manefest 文件里面注册这个我们写好的 Service :
|
|
客户端代码
前面说过,在客户端我们要完成的工作主要是调用服务端的方法,但是在那之前,我们首先要连接上服务端,完整的客户端代码是这样的:
|
|
AIDLActivity 是客户端代码,首先bindService建立连接,然后在 ServiceConnection 里面获取 BookManager 对象,接着通过它来调用服务端的方法。
3、注意事项
- 在使用AIDL进行跨进程通信时,在调用远程进程方法时,尽量在子线程处理,避免远程进程方法做了耗时操作,阻塞自己的UI线程。
- 服务端需要处理并发问题。
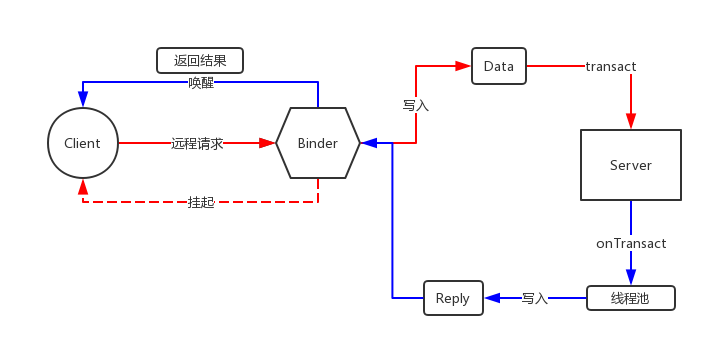
四、AIDL工作原理
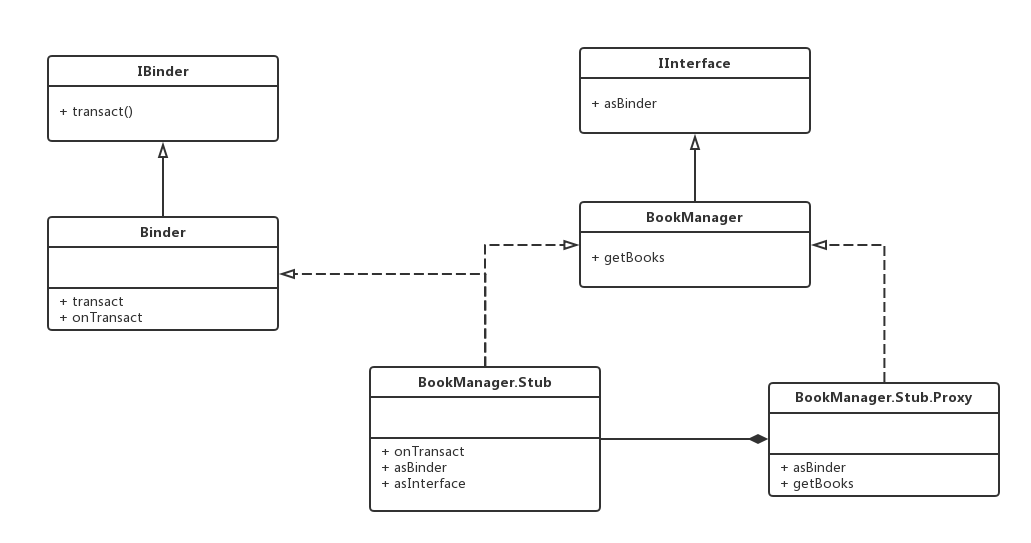
五、AIDL结构类图
代码地址
https://github.com/atopom/android_first_draft/tree/master/Code/IPC%E9%80%9A%E4%BF%A1